Drones make life easier for everyone. Or how do you explain an unmanned drone providing relief assistance to victims of disasters? Truly an amazing piece of modern technology.
Of course, many are bewildered by how capable drones are but they mostly don’t know how they work. So, how do drones work? That’s what you’re about to find out in this article. Drones use different mechanical features to operate and deliver goods. Some of those features include rotors, motors, a flight controller, a gyroscope, an accelerometer, and more. Besides, drones can be personal or military and you’re probably asking yourself; “how do military drones work? How do personal drones work?” You’re about to get the answers you seek. Read on as we lay bare everything you need to know about how drone technology works.
Drone anatomy
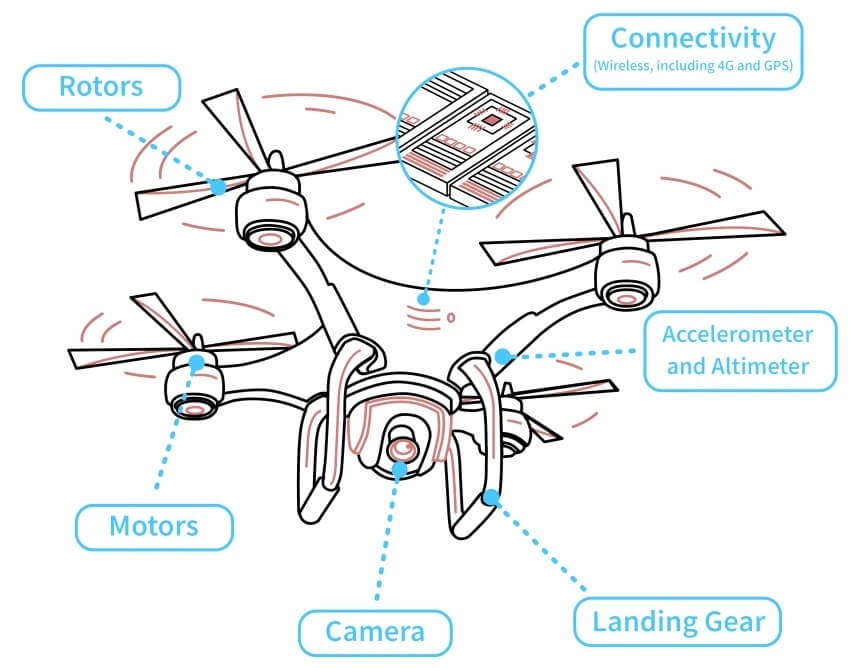
Flight controller
The United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) describes drones as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). So, how do drones operate since they’re unmanned? Trust us, that’s not a miracle either. They’re able to operate thanks to the help of a flight controller.
The flight controller essentially works as the drone’s “brains”. It is responsible for receiving information from the remote controller, obstacle avoidance sensors, GPS, etc., and relaying it to the motors to carry out the instructions. For example, if you were flying a drone and pressed a turn on the controller, you would be transmitting a signal to the flight controller to turn the drone in your preferred direction.
Moreover, controlling a stunt drone like the Sky Viper Fury can be fun. The drone provides eight one-touch stunts and 360° flips from a stationary hover. And that’s not to mention the impressive surface scan technology that offers stable flight. If this machine doesn’t tickle your fancy, there are still top stunt drones you can choose from.
Rotors
Rotors are responsible for the vertical motion of a drone. The drone uses the rotors, typically consisting of a propeller connected to a motor, to hover and take images or anything you want it to do at a high altitude. The drone hovers when two of its four rotors move in a clockwise direction while the others move in an anticlockwise direction, ensuring the balance of the drone’s sideways momentum.
Motors
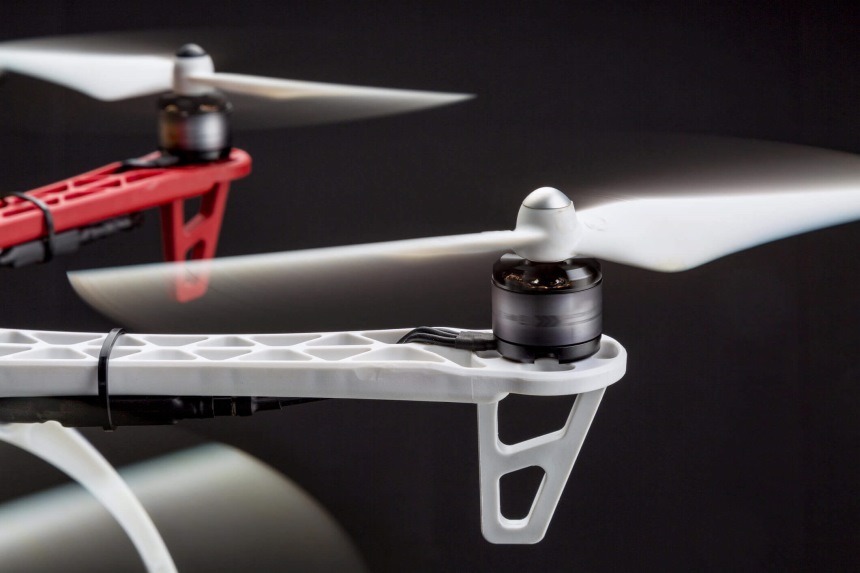

Besides, drones typically come in two different motors—brushed and brushless. The brushed motors are traditional and lay the foundation for standard motor technology. A brush motor uses a central rotor that is surrounded by a stator lined with a pair of magnets. Brushed motors, on the other hand, use a centrally-located stator surrounded by a rotor lined with a set of magnets. They’re considered a more efficient alternative.
Altimeter and accelerometer
The altimeter and accelerometer are also crucial to the operation of a drone. Both components work together. While the accelerometer tells the drone about its direction and speed, the altimeter feeds the machine information about its altitude. Thanks to these features, the drone can land slowly without incident.
Landing gear
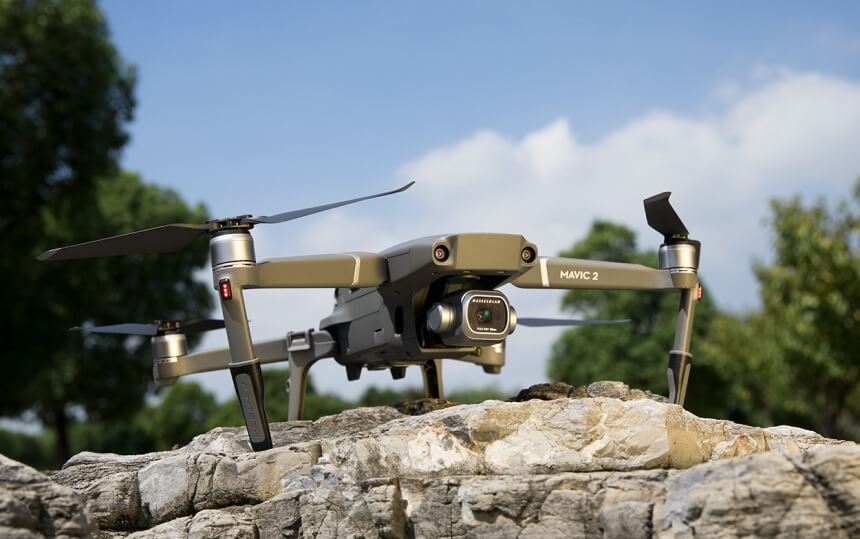

Cameras
Drones are most popular for taking aerial photos. For example, personal drones can be deployed to take pictures of properties. Military drones also take pictures of targets, mostly for spying purposes. Both types of drones can’t take pictures without the cameras built inside them. The cameras are typically placed beneath the drones, centrally.
With these cameras, pilots can easily capture nice photos. For example, the DJI Mavic Air 2 captures impressive 48MP photos with a 1/2 -inch CMOS sensor while its 3-axis gimbal provides 4K/60fps video. That’s on top of the 34 minutes of flight time.
Drone working processes
After knowing the working components of a drone, the next step is knowing the working processes, including how it flies, how it avoids obstacles, and how it takes pictures and videos. Rest assured, we’ll provide you all the necessary information below:
How drones fly in different directions
It’s not unusual for anyone to wonder how drones fly. Some may consider it a miracle but we’d like to describe it as physics in action. Remember we mentioned earlier how motors and propellers work together. Well, they’re responsible for drones flying. The motors spin the propellers while the latter pushes against the air molecules to get the drone moving.
You’re still in the dark? Okay, picture yourself swimming. Can you see yourself cupping your hands and using them to push against the water while your body moves forward? That’s similar to how drones fly! By pushing the air molecules downward with their spin, the propellers inadvertently pull the drone upwards.
How drones avoid obstacles
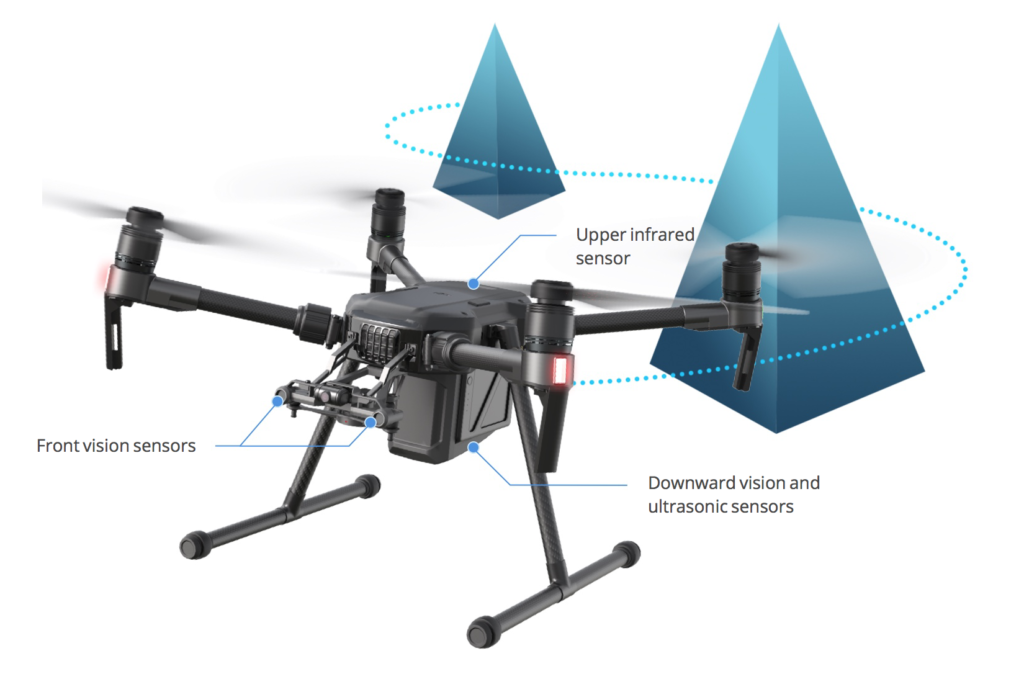
If the path is not changed, the drone will stop and hover until the pilot directs it away from the obstacle. The sensors are common features in the best drones for roof inspections.
How drones take videos and photos
As we said before, drones take photos and videos but how do they go about it? They use built-in, high-end cameras to shoot photos and videos. With the help of special devices known as “gimbals”, the cameras stay in place to take smooth aerial shots while the drones move around. The pilot uses a controller to record the videos and capture the photos.
Besides, if you’d like a lightweight drone to avoid FAA’s weight restrictions, you could find the ideal choice for taking great videos and photos among the best drones under 250 grams.
Final Thoughts
Without any doubt, drones showcase the beauty of technology. These machines offer a wide range of benefits. For example, per CNN Trusted Source In the future, drones could save your life | CNN Are fast-flying drones the future of emergency medicine? Here’s why some researchers say drones could beat ambulance times and help save lives. www.cnn.com , researchers at William Carey University in Mississippi suggested that disaster drones could carry medical kits to victims of a mass casualty incident before the arrival of an ambulance.
The most frequently asked question is; how do drones work? As we’ve carefully explained in this article, drones combine different components and technologies to fly and operate. If you’ve always wondered how drones can fly and take photos, this article provides you all the right information to get out of the dark as far as drone technology is concerned.












